The Software Testing Life Cycle
The software testing lifecycle (STLC) lays out a series of steps to create and execute software tests. It is analogous to the software development lifecycle which lays out a series of steps to plan and develop software artifacts.
The benefits of using the STLC include:
- It provides a guide for the testing process, increasing efficiency and consistency,
- It clearly defines the expectations of each part of the project,
- It can provide time constraints on the testing,
- Ensures that software meets requirements before more software is developed,
- Ensures that all project requirements are met.
The major steps in the software testing lifecycle are shown in the following diagram.
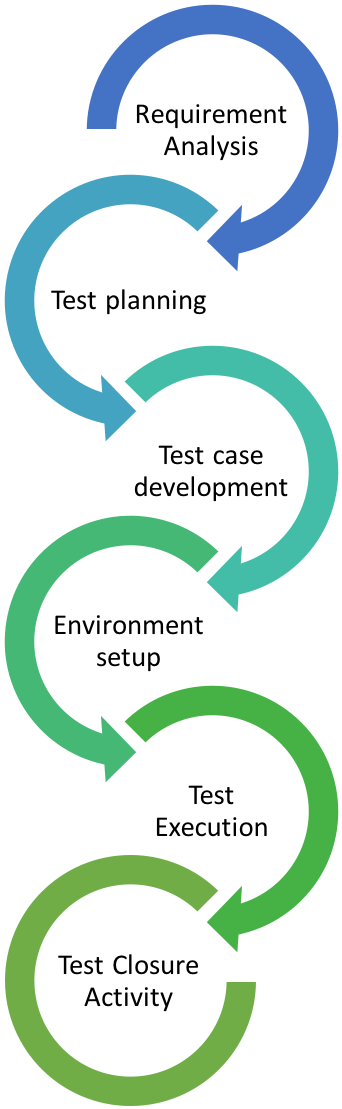
STLC Phases
We will now look at each of the phases of the STLC in depth.
Requirements Analysis
As the project requirements are identified, these requirements are examined to identify their testable aspects. The requirements can be either functional or non-functional and we will identify what needs to be tested for each of the requirements.
Entry Criteria - A set of requirements and acceptance criteria for the requirements.
Exit Criteria - Requirements traceability matrix and an automation feasibility report. The traceability matrix will show how each test relates to each requirement while the automation feasibility report will layout the plans and possibility of automating the testing.
Requirements Traceability Matrix
Traceability is important in large projects. For example, one aircraft software system had a requirements document that ran to 800 pages. There are two problems that need to be addressed in projects of this size:
- Ensuring that software has been written to implement each of the requirements,
- Ensuring that tests have been developed to test all of the software written for each requirement.
The following is an example of a requirements traceability matrix.
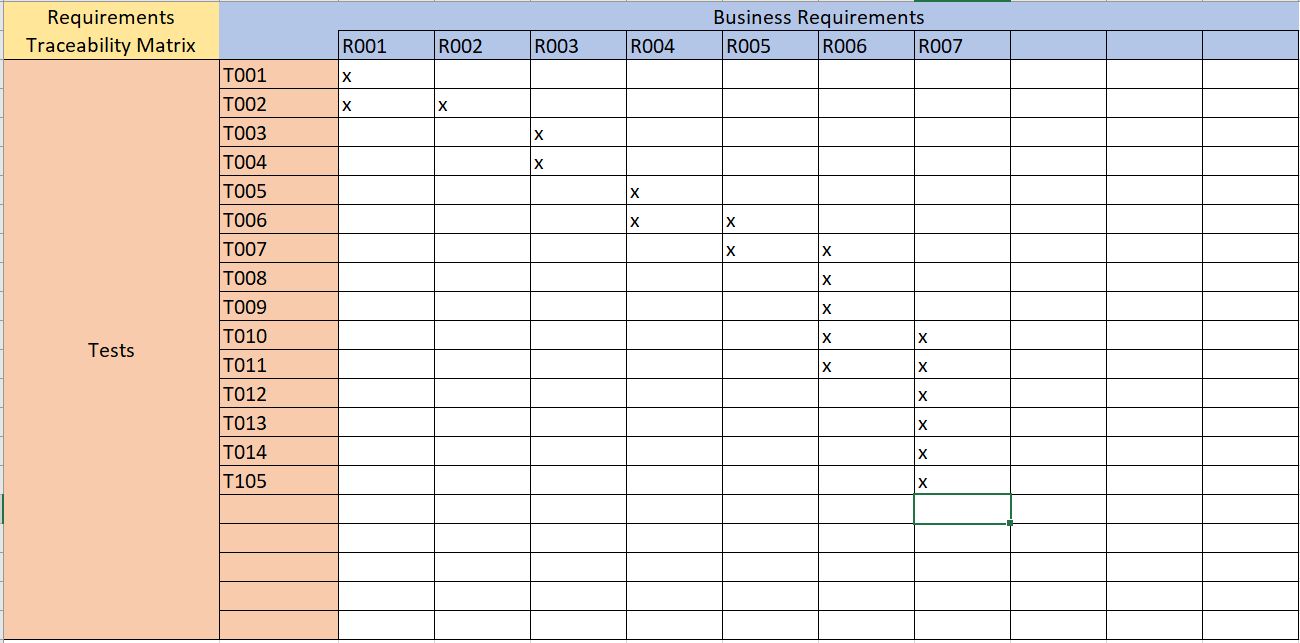
The matrix lists the business requirements across the top and the tests down the left side. The x's in the matrix indicate that the tests are associated with the requirements. This let's you easily see which tests apply to which requirements and vice versa. The table allows you to do forward traceability where you look up a requirement and find the related tests as well as reverse traceability where you look up a test and see the associated requirements.
Test Planning
The test planning phase produces the test plan document. This document includes the testing strategy, the testing steps, the tools needed for the testing, and the roles and responsibilities in the quality assurance team. It also provides an estimated timeline for the testing
Entry criteria - the requirements analysis and requirements test matrix,
Exit criteria - an approved test plan.
Test case development
It is during this phase that the actual test cases are created each test case defines:
- Input data for the test case,
- The actual code for the test,
- Procedures for executing the test case,
- Anticipated results of the test case.
It is during this phase that automation scripts will be created if they are needed.
Entry criteria - an approved test plan.
Exit criteria - approved test cases, test data, and automation scripts if needed.
Test Environment Setup
It is during this phase that the test environment is set up. This might include testing tools, integration with version control systems, and any other hardware and software necessary to conduct the testing.
Entry criteria - system design and project architecture.
Exit criteria - a functional test environment.
Test Execution
During the test execution phase, the tests are deployed into the testing environment and then are executed using the input data. The expected test results are compared to the actual results and gathered to create a report which was sent to the development team.
Entry criteria- all of the exit criteria from the previous steps.
Exit criteria - all of the tests have been performed and test reports have been generated.
Test Cycle Closure
This is the final phase of the STLC and it results in a report which summarizes the results of all the tests which were carried out. The report should contain:
- A summary of the entire testing process,
- A list of tests that failed along with the comparison of the expected results and the actual results,
- the time taken to conduct the testing,
- the total costs of the testing,
- The test coverage,
- and a description of the defects found.
Entry Criteria - test results and reports.
Exit criteria - test closure report.